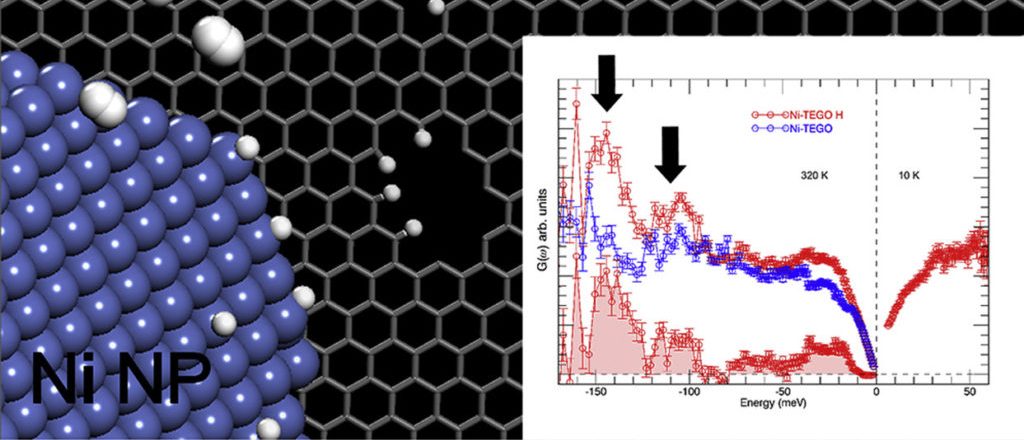
Surface decoration of graphene-based nanostructures with metals has been predicted to be an efficient way towards the development of resistant catalysts and novel materials for energy applications, such as hydrogen production and storage. We report on an extensive neutron scattering study of a defective graphene-based material decorated with nickel nanoparticles, obtained via the chemical decoration of thermally exfoliated graphite oxide. The combination of neutron diffraction and inelastic neutron scattering measurements has been used to characterize the low-dimensional carbon backbone and the presence of the nickel nanoparticles, organized at the nanometer scale on the graphene plane. The structural features of this system, along with the nickel capability of dissociating the hydrogen molecule upon hydrogen treatment, are herein discussed.
Reproduced with permission. Copyright 2020, Elsevier